Lentils, once seen as a simple meat substitute, have emerged as a nutritional powerhouse in modern cuisine. These small legumes are not only a rich source of plant-based protein but also come packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Their health benefits extend beyond just being a nutritious food source, offering potential protection against various chronic diseases.
Ingredients of Wellness: Lentils
Lentils have been a staple in many cuisines for centuries, but their health benefits are making them increasingly popular in contemporary diets. These legumes are gluten-free and offer a plethora of vitamins and minerals without the fat or cholesterol associated with red meat.
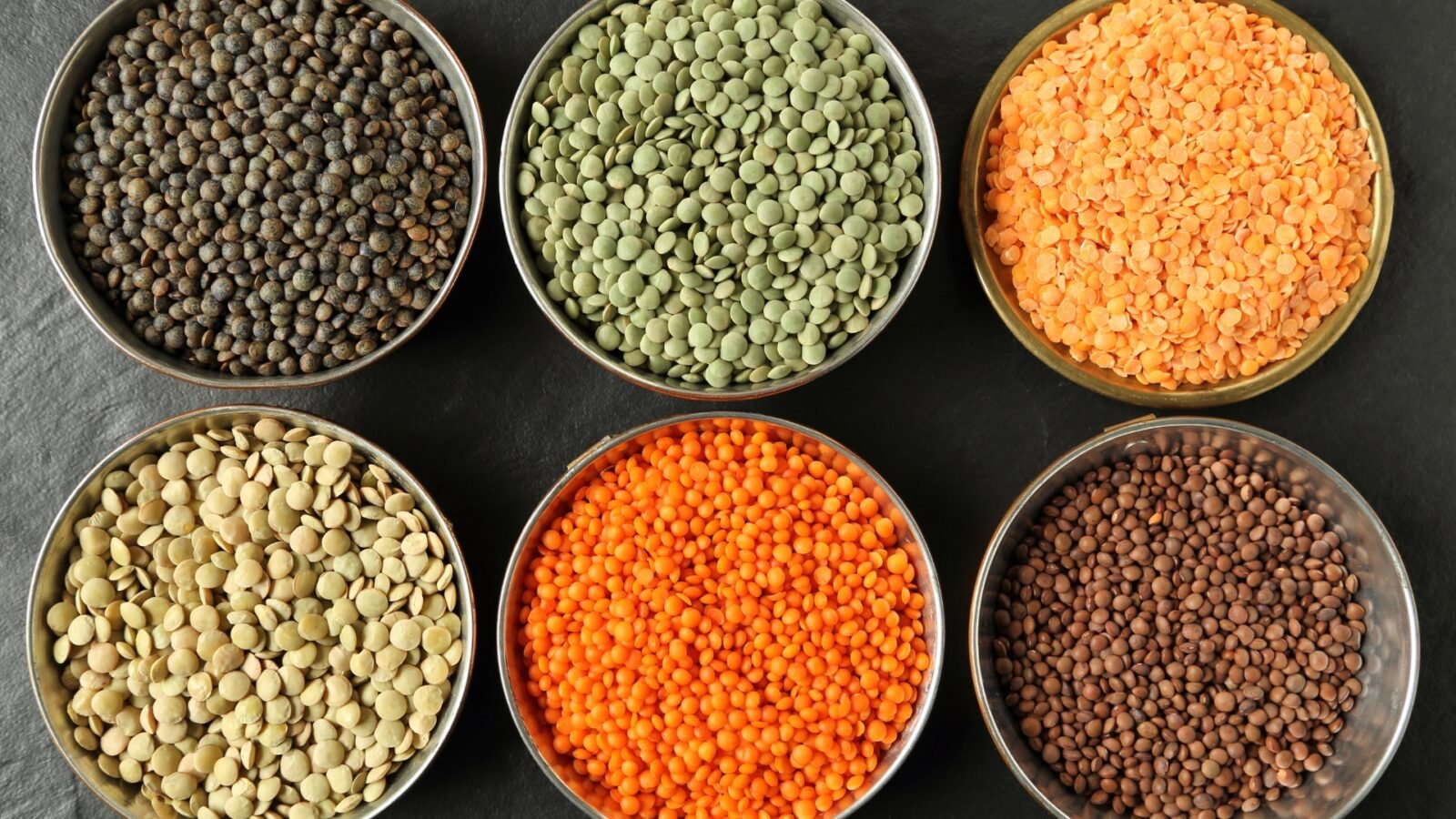
Dietitian Elyse Homan highlights that lentils are not just an affordable meat alternative but can be the cornerstone of numerous dishes, contributing significantly to our health. Lentils come in various types, including brown, green, red, and black, each with its unique taste and culinary use.
Five Health Benefits of Lentils:
1. Disease Protection: Regular consumption of lentils can potentially reduce the risk of chronic ailments like diabetes, obesity, heart disease, and certain cancers. The polyphenols in lentils exhibit anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties. These compounds might also aid in improving cholesterol levels, especially in diabetic individuals.
2. Blood Pressure Regulation: Lentils are a good source of potassium, which counteracts the effects of sodium, helping to manage blood pressure. Their high protein content also makes them an excellent alternative to red meat.

3. Heart Health Enhancement: Lentils are rich in folate, iron, and vitamin B1, all of which support heart health. They may also help in reducing bad cholesterol and blood pressure, further promoting cardiovascular health.

4. Energy Boost: Lentils provide a decent amount of iron, essential for producing hemoglobin in our red blood cells, which carries oxygen throughout the body. This can be particularly beneficial for those with anemia or those following a vegan or vegetarian diet.

5. Digestive Support: The fiber in lentils aids digestion and promotes gut health. It also plays a role in bowel regulation and immune system protection.
Considerations When Consuming Lentils:
While lentils are generally safe and beneficial for most, overconsumption or eating them undercooked can lead to digestive issues like gas and cramping. It’s advisable to increase fiber intake gradually to minimize these effects. Lentils also contain anti-nutrients that can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals, but proper soaking and cooking can mitigate this. A small fraction of people might be allergic to lentils, so it’s essential to be cautious if you have known legume allergies.
Preparing and Storing Lentils:
Lentils are relatively easy to prepare. Unlike many beans, they don’t require overnight soaking. Simply rinse them to remove any impurities and cook. Depending on the type, cooking times can vary. Lentils can be incorporated into various dishes, from salads to soups. Once cooked, they can be stored in the refrigerator for about a week or frozen for up to three months.
Lentils: A Nutritious Addition to Your Diet:
Lentils are a versatile and nutritious addition to any diet. Their myriad health benefits make them a must-have in your pantry. Whether you’re looking to boost your protein intake, improve your heart health, or simply enjoy a delicious and hearty meal, lentils are the way to go.














Leave a Review